
Deep sedation is done by administering the drug via an IV while the patient is lying down. Deep sedation is much stronger than conscious sedation and therefore requires the presence of an anaesthesiologist who will inject the sedative in a continuous, controlled manner throughout the entire procedure. For this reason deep sedation is often referred to as anaesthesia.

Deep sedation or anaesthesia: is a type of sedation which causes the patient to fall into a deep sleep, therefore eliminating any and all discomfort or pain.

In certain cases (or on the request of the patient), stronger sedatives may be used, therefore any discomfort will be lessened even further. This type of sedation is done using analgesic or hypnotic drugs, and is intended to calm the patient and have them relax, even if it will not put them to sleep completely.
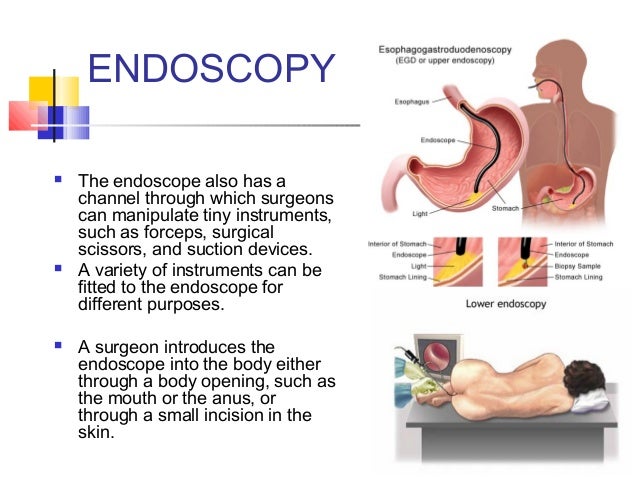
Conscious sedation: is a mild sedative which is taken orally (in drops or pills), normally a few minutes prior to beginning the Endoscopy. Here is a list of different methods of sedation: During the examination gas or water may be injected so as to provide better visualization of the organs.Ī Gastroscopy is known to be an invasive test which may often require sedation, especially if done using a traditional method. What the camera records within the organs will appear on a screen, ready to be analysed in detail by the doctor. The doctor or assistant will begin to insert the gastroscope into the patient’s mouth. The patient is asked to lie down on their left side. Endoscopy is normally done in an outpatient situation and therefore does not require admission to hospital. This time frame can vary based on certain factors: if the examination does not include any surgical procedures the time required will be far less. The exam can last anywhere from 10 to 15 minutes. All other medications which are normally taken, can continue to be taken except if the specialist sees fit otherwise. The specialist will consider the temporary interruption of these medications, for how long and in what way. For patients taking anticoagulant or blood thinning medications they must inform the endoscopy centre at least 7 days prior to the exam, especially if a biopsy, the removal of polyps, or other surgical procedures are scheduled or probable. Also medications which are “ proton pump inhibitors” must be interrupted up to 5 days prior to the exam For all patients: do not take antacids or sucralfate the day prior to the exam. Here is a list of foods to avoid and those that are permissible: They can however have a light breakfast, preferably plain biscuits, fruit juice, camomile or tea.Īs for the evening prior to the exam, it is suggested that the patient have a light dinner, preferably a vegetable broth. If the procedure is in the afternoon, the patient will still need to fast at least 5 hours prior to the procedure. High blood pressure medication) with very little water. The patient can however continue to take their normally required prescription medication (ex. The patient must fast from 12 o’clock midnight the night prior to the procedure, and therefore cannot eat or drink anything solid or liquid, not even water. The preparation for a gastroscopy includes a proper diet. By using tools which are located within the endoscope, it’s possible to remove samples of tissues, in other words biopsies, carry out minor surgery, stop bleeding and finally perform emergency interventions. Traditional or transnasal endoscopies even allow the medical specialist to perform surgical procedures, so called operations. In general, the problems for which a Gastroscopy may be requested are the following: It can be requested for all the problems associated with the upper part of the digestive tract, as it provides the doctor with a clear and direct visual of the area during the examination, thanks to high definition, colour images. What is a Gastroscopy used for?Ī Gastroscopy is prescribed for various reasons and represents one of the best diagnostic tools available in the medical field today. A Gastroscopy is a medical examination, also called Upper GI Endoscopy or Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, which examines the inside of the upper part of the digestive tract, made up of the stomach, oesophagus, and duodenum normally up to the second portion of it.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
